|
Winterschool: Nanotechnology for the design of functional materials:
|
|
| TU Dresden » ... » Chemie und Lebensmittelchemie » Physikalische Chemie und Elektrochemie » Arbeitsgruppe für Theoretische Chemie » NDFM 2012 |
NAVIGATION
---------------
 General Information
General Information
 Latest News
Latest News
 Location
Location
 Topics
Topics
 Program
Program
 Application
Application
 Organization & Funding
Organization & Funding
 Poster
Poster
 Contact
Contact
High-Resolution Structural Characterization of Nanoscale Materials
Christian Kübel - Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute of Nanotechnology
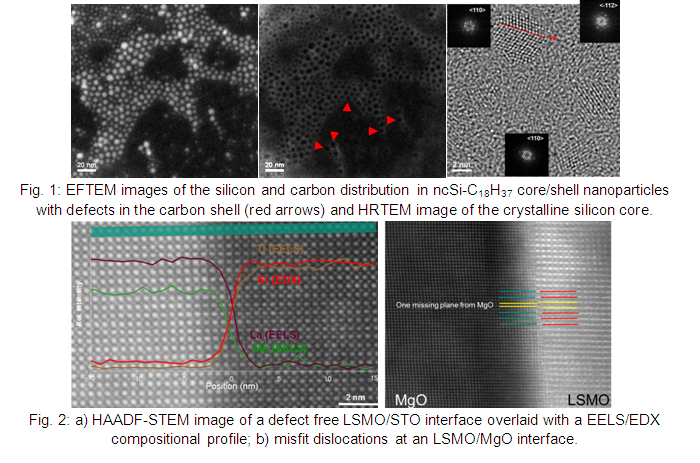
A fundamental understanding of the correlation between synthesis, structure and properties is necessary for systematic new developments in nanotechnology. Considering structural characterization, electron microscopy techniques are very powerful, providing direct images of nanomaterials with up to atomic resolution in 2D and 3D, which can be further combined with sub-nanometer scale semi-quantitative compositional information. This makes electron microscopy techniques one of the essential characterization techniques in nanotechnology. With this course, we will provide an introduction to electron microscopy for materials analysis: Starting with basic electron optics and image/signal formation inside a transmission electron microscope (TEM) and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) will provide the necessary background to introduce different application areas in the second part of the course, illustrating the possibilities that electron microscopy offers for structural and compositional characterization. For this we will introduce SE/BSE imaging in the SEM/FIB and BF/DF imaging, electron diffraction and aberration corrected high-resolution imaging in TEM and STEM. Analytical techniques (EDX and EELS) will be introduced as well as also some of the more recent microscopy developments such as electron tomography, orientation imaging and in-situ experiments. For the application part, SEM and TEM sample preparation will be discussed followed by extensive examples covering a wide range of materials characterization from CNTs/graphene to clusters and nanoparticles (Fig. 1), polymer nanocomposites and finally thin film device structures (Fig. 2). Special emphasis will also be paid to the complementarity of electron microscopy techniques and alternative characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction/spectroscopy and scanning probe techniques.