The wavefunctions of the adsorbed guest are represented on a
finite uniform spatial grid. The maximum kinetic energy of the guest, which can
be represented in this solutions is therefore limited to
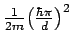 ,
where
,
where 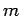 is the mass
of the guest, and
is the mass
of the guest, and 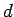 is the coarsest grid spacing. For grid spacings of
is the coarsest grid spacing. For grid spacings of 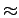 0.7 bohr,
typically used in the following (see Chapter 3 and below) simulations,
this condition implies a kinetic energy cutoff of
0.7 bohr,
typically used in the following (see Chapter 3 and below) simulations,
this condition implies a kinetic energy cutoff of 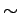 850K.
As the primarily interested temperatures are
850K.
As the primarily interested temperatures are 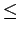 300K, the impact of the finite
basis representation is not severe and it is further reduced by the
counter-poise correction, as discussed above.
300K, the impact of the finite
basis representation is not severe and it is further reduced by the
counter-poise correction, as discussed above.
Lyuben Zhechkov
2007-09-04