Physisorption on graphene
In the previous chapter it has been shown that the H2 C
C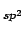 pair potential can be parametrised on simple H2
pair potential can be parametrised on simple H2 PAH models.
Such a potential has been used to evaluate the hydrogen interaction with different PAH structures and the rest have been extrapolated towards graphene platelets.
The still remaining important questions are:
How does the temperature influence the weak H2
PAH models.
Such a potential has been used to evaluate the hydrogen interaction with different PAH structures and the rest have been extrapolated towards graphene platelets.
The still remaining important questions are:
How does the temperature influence the weak H2 sorbent interaction (
sorbent interaction (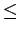 10 kJ
10 kJ mol
mol ) and how can the H2
) and how can the H2 H2 interactions be taken into account.
The following chapter is intended to answer these questions and to give an example how the mathematical machinery described in Chapter 1 works in practice.
The systems investigated in this chapter are graphene monolayer and graphene slit pores confined with different graphene interlayer distance.
H2 interactions be taken into account.
The following chapter is intended to answer these questions and to give an example how the mathematical machinery described in Chapter 1 works in practice.
The systems investigated in this chapter are graphene monolayer and graphene slit pores confined with different graphene interlayer distance.
Subsections
Lyuben Zhechkov
2007-09-04